C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Quantitative

Gender for
Male, Female

Report Tat
2HRS Same Day
No special preparation

Sample Type
SERUM
Test Overview
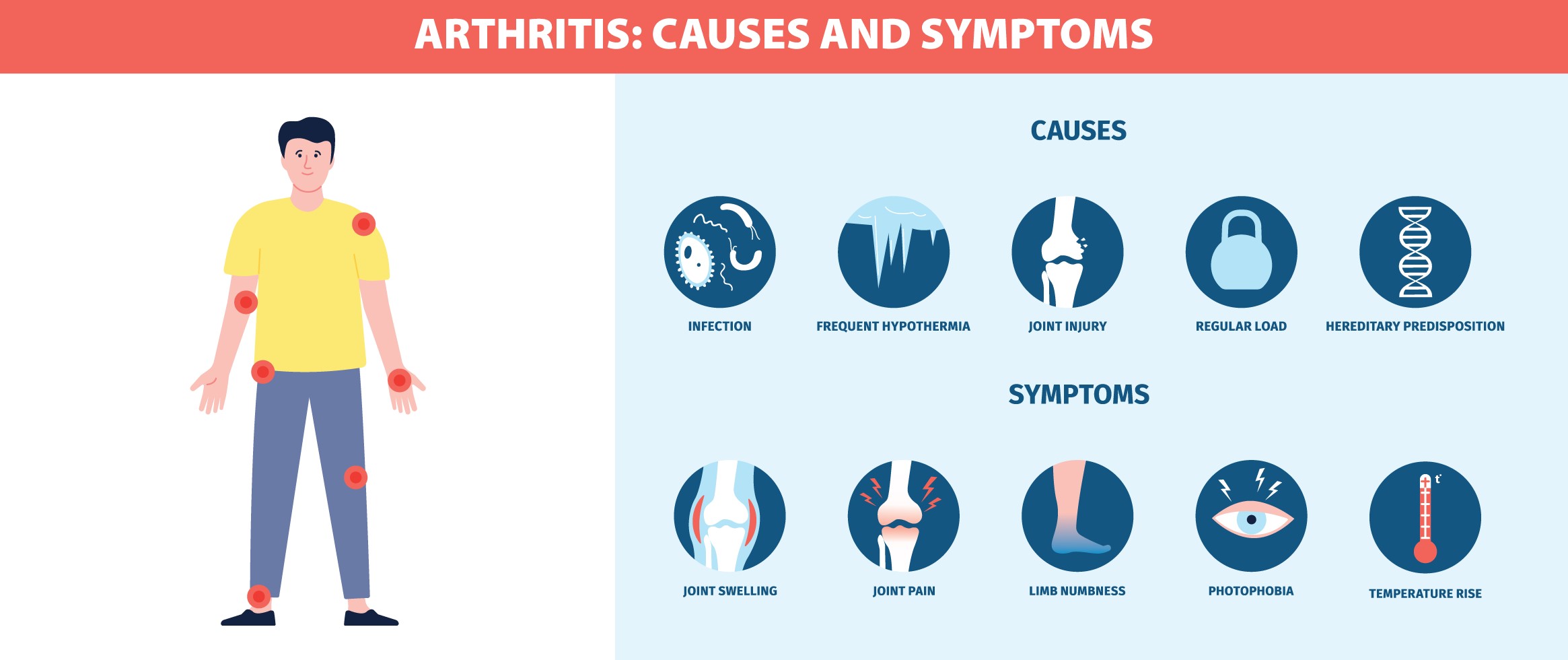
The C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Quantitative test measures the level of CRP in the blood, a protein that increases when there’s inflammation in the body. High CRP levels may indicate an infection, inflammation, or other underlying health conditions. This test is useful for monitoring chronic inflammatory diseases, such as arthritis, and assessing risk levels for heart disease.

 NABL approved
NABL approved Labs
 Most Trusted by
Most Trusted by Doctors
 Accuracy &
Accuracy & timely reporting
 Widest Range
Widest Range of Tests
Test Details
Frequently asked questions
This test measures the level of C-Reactive Protein in the blood to identify inflammation or infection.
No special preparation is required, but it’s advisable to inform your healthcare provider about any medications.
Results are generally available within 24 hours.
Yes, the CRP Quantitative test can be booked online through Pathkind Labs for home collection or at a nearby center.
High CRP levels may indicate infection, chronic inflammatory diseases, or an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.

















.png)
.png)
