The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a diagnostic test that measures the rate at which red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle in a tube of blood. The ESR test is a simple and non- invasive test that requires only a small sample of blood, usually drawn from a vein in your arm. The ESR test measures the rate at which red blood cells sediment, or settle, in a tube of blood. The rate is influenced by the amount of protein, specifically fibrinogen, in the blood. Fibrinogen is a protein that helps the blood clot and is produced by the liver.During the ESR test, a small sample of blood is collected and placed in a tube that is then placed vertically in a machine called a Sedimentation Rate Analyzer. The rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is then measured and reported in millimeters per hour (mm/hr).
The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) is a diagnostic test that measures the rate at which red blood cells (erythrocytes) settle in a tube of blood. The ESR test is a simple and non- invasive test that requires only a small sample of blood, usually drawn from a vein in your arm. The ESR test measures the rate at which red blood cells sediment, or settle, in a tube of blood. The rate is influenced by the amount of protein, specifically fibrinogen, in the blood. Fibrinogen is a protein that helps the blood clot and is produced by the liver.During the ESR test, a small sample of blood is collected and placed in a tube that is then placed vertically in a machine called a Sedimentation Rate Analyzer. The rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is then measured and reported in millimeters per hour (mm/hr).
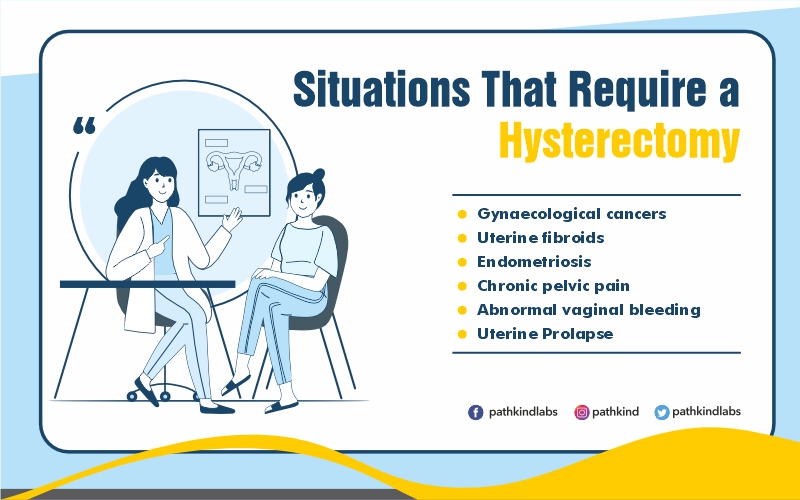
Why is Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test Done?
The ESR test is usually performed as a part of a routine health check-up or if you have symptoms that may indicate an underlying condition, such as fever, fatigue, weight loss, or joint pain. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for certain conditions, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.The ESR test is a screening test that can help your healthcare provider determine if you have an underlying condition that may require further evaluation or treatment. However, the ESR test is not specific to any particular condition and cannot be used to diagnose a specific condition. Other diagnostic tests, such as blood cultures, imaging tests, or biopsies, may be needed to confirm a diagnosis.
Who Should Get Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test?
The ESR test is typically recommended for adults with symptoms that may indicate an underlying condition, such as fever, fatigue, weight loss, or joint pain. It is also recommended for individuals with a history of certain conditions, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancer, to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.Your healthcare provider may also recommend the ESR test if you are taking certain medications, such as corticosteroids, that can affect the rate at which red blood cells sediment.
How to Prepare for Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test?
To prepare for the ESR test, you will be asked to fast for 9-12 hours before the test. This means you should not eat or drink anything except for water during this time. Your healthcare provider may also ask you to stop taking certain medications, such as corticosteroids, before the test.
What to Expect During Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test?
The ESR test is a simple and non-invasive test that requires only a small sample of blood, usually drawn from a vein in your arm. The blood sample is collected using a needle and syringe, which may cause a slight pinching sensation. The sample is then placed in a tube and placed vertically in a Sedimentation Rate Analyzer. The ESR test is a quick and relatively painless procedure that takes only a few minutes to complete. The results of the test are usually available within a few hours or a day.
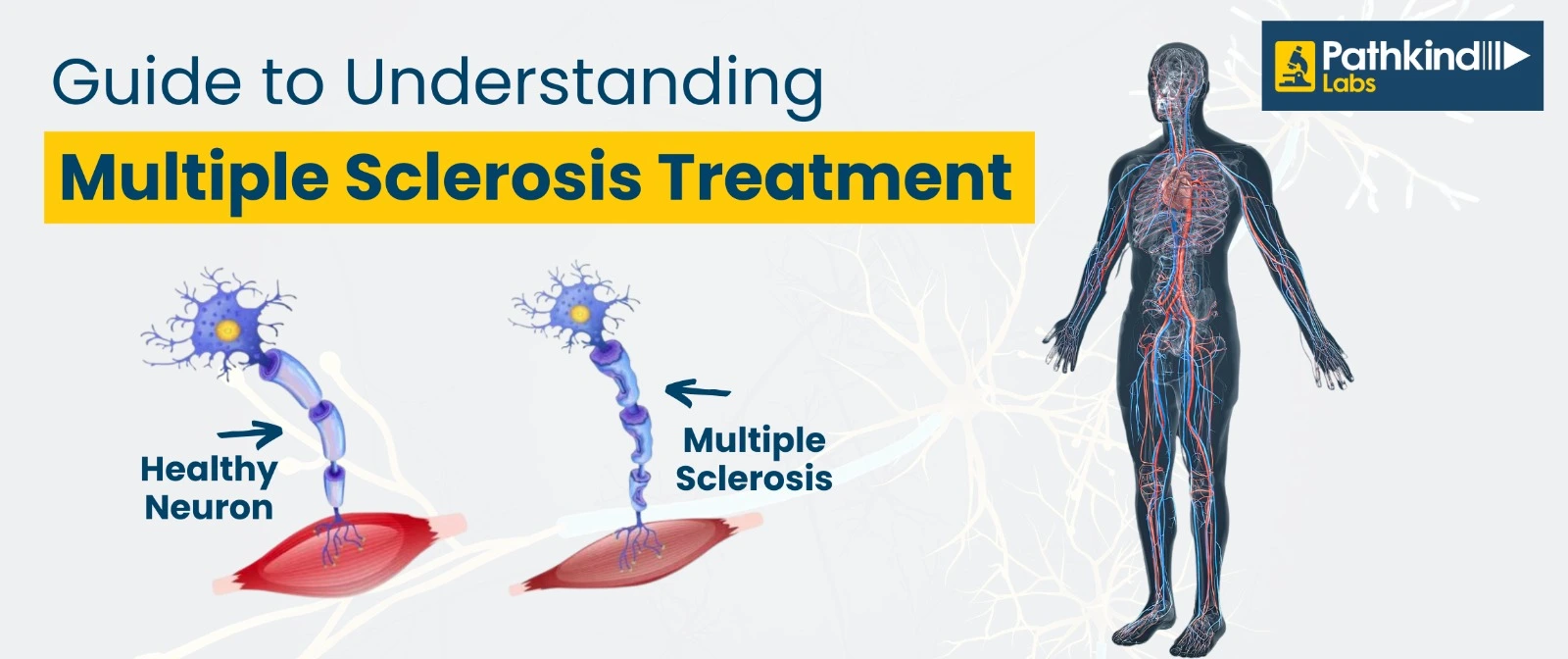
What Does Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Test Measure?
The ESR test measures the rate at which red blood cells sediment, or settle, in a tube of blood. The rate is influenced by the amount of protein, specifically fibrinogen, in the blood. Fibrinogen is a protein that helps the blood clot and is produced by the liver.
- Red Blood Cell Sedimentation Rate During the ESR test, a small sample of blood is collected and placed in a tube that is then placed vertically in a machine called a Sedimentation Rate Analyzer. The rate at which the red
blood cells settle to the bottom of the tube is then measured and reported in millimeters per hour (mm/hr).
The ESR test measures the rate at which red blood cells sediment, or settle, in a tube of blood. The rate is influenced by the amount of protein, specifically fibrinogen, in the blood. Fibrinogen is a protein that helps the blood to clot and is produced by the liver.
- Normal Range for ESR A normal ESR result is typically less than 20 mm/hr for women and less than 15 mm/hr for men. However, the normal range may vary depending on age, sex, and other factors.
- Abnormal ESR Results A higher-than-normal ESR result may indicate an underlying condition, such as inflammation, infection, or cancer, while a lower-than-normal ESR result may indicate a deficiency in
fibrinogen or other blood clotting factors.
- Interpreting ESR Results Your healthcare provider will interpret your ESR test results in the context of your overall health and any symptoms you may be experiencing. They will consider factors such as your age, sex, and other medical conditions when interpreting your results.
It is important to note that the ESR test is only a screening test and cannot be used to diagnose a specific condition. Other diagnostic tests, such as blood cultures, imaging tests, or biopsies, may be needed to confirm a diagnosis.
When to Call a Doctor?
You should contact your healthcare provider if you have any symptoms that may indicate an underlying condition, such as fever, fatigue, weight loss, or joint pain. Your healthcare provider will determine if the ESR test is necessary and can explain the results of the test to you. If you are being treated for an underlying condition and have abnormal ESR test results, you should also contact your healthcare provider. They can assess the results and determine if any adjustments to your treatment plan are necessary.




 NABL approved
NABL approved  Most Trusted by
Most Trusted by  Accuracy &
Accuracy &  Widest Range
Widest Range 

















.png)