Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Detector, Qualitative

Gender for Male, Female

Report Tat
Tues, Thurs, Sat 7.30 PM
Clinical History In Specified

Sample Type
1.5 ml EDTA Plasma. Separate Plasma within 2 hrs of collection by centrifuge at 1800g for 10-12 min. Kindly ship along with Cold packs to maintain temperature of 4- 15°C
Test Overview
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Detector, Qualitative Test
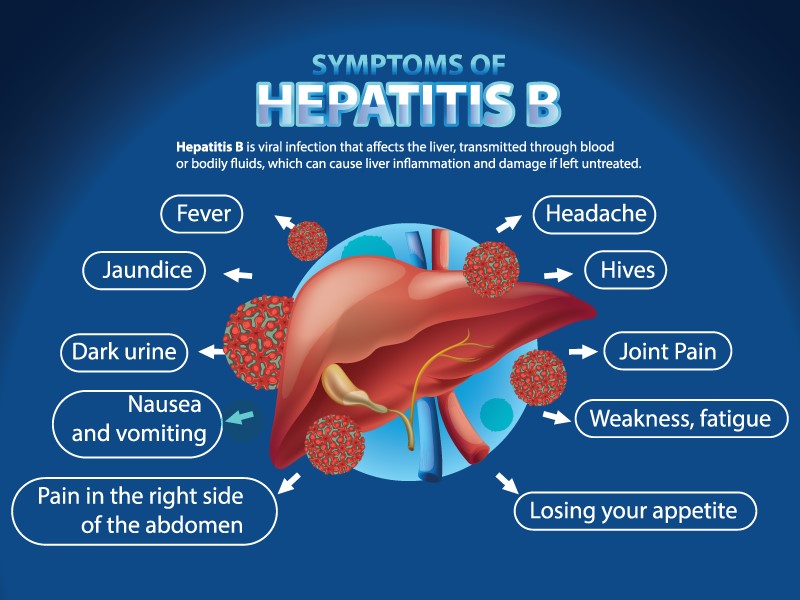
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Detector Qualitative test reveals the Hepatitis B virus's presence in the body. Hepatitis B damages the liver, leading to severe problems like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Detecting the virus early is crucial to control and avert these complications. This test is made to check for the genetic material of the Hepatitis B Virus in samples from patients, like blood or serum. Unlike other tests that look for antibodies the body makes to fight the virus, the HBV DNA Detector looks directly for the virus's DNA. This makes the diagnosis more accurate and sensitive.

 NABL approved
NABL approved Labs
 Most Trusted by
Most Trusted by Doctors
 Accuracy &
Accuracy & timely reporting
 Widest Range
Widest Range of Tests
Test Details
Frequently asked questions
The HBV DNA Detector is not a replacement but complements serological tests. While serological tests detect antibodies, this qualitative test directly identifies Hepatitis B Virus DNA, providing a more precise diagnostic tool.
The test assists treatment decisions by confirming active viral replication, helping healthcare providers tailor interventions, monitor therapy effectiveness, and mitigate the risk of severe liver complications associated with Hepatitis B.
Yes, the test is valuable for routine screening as it enables early detection of Hepatitis B Virus DNA, contributing to timely intervention and public health efforts to control the spread of the infection.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology amplifies and detects small amounts of Hepatitis B Virus DNA in patient samples, ensuring a highly sensitive and accurate qualitative test result.
Early detection with the HBV DNA Detector facilitates timely medical care, potentially preventing the progression of Hepatitis B infection to more severe liver diseases and improving overall patient outcomes.
The test is valuable for monitoring antiviral therapy effectiveness by assessing the presence or absence of active viral replication, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about treatment adjustments.
Absolutely, the test is applicable for population-based studies, aiding in epidemiological research and contributing to a better understanding of the prevalence and dynamics of Hepatitis B infections.
The test contributes to global control efforts by enabling early diagnosis, facilitating targeted interventions, and reducing the burden of Hepatitis B-related complications on public health systems.
While it is primarily conducted in clinical laboratories, ongoing advancements may lead to adaptations for point-of-care use, potentially broadening access to timely Hepatitis B detection in diverse healthcare settings.