Liver Function Test (LFT) Test Overview
Blood tests for liver function tests measure the proteins, enzymes, and bilirubin your liver produces. Different chemicals can signal various diseases by having high or low quantities.
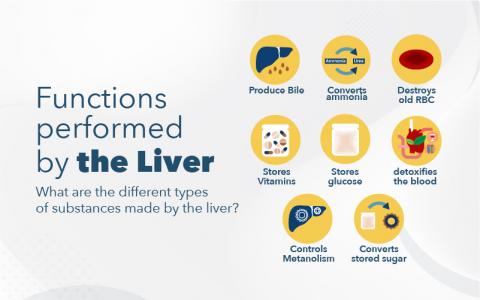
The liver is a large organ located in the upper right of the belly; the liver is essential for a variety of processes. For instance, it breaks down drugs and alcohol, filters hazardous compounds, stores vitamins and minerals, and produces bile, proteins, and enzymes in addition to other functions. Liver Function Test (LFT) Tests look at proteins, enzymes, and other elements that reveal how efficiently the liver operates. They can demonstrate whether there is liver cell injury or an obstruction of the liver's blood supply.
The liver filters all blood that exits the stomach and intestines. The liver processes this blood, breaking down, balancing, and creating nutrients, as well as metabolising medications into forms that are easier for the rest of the body to use or are harmless.
Liver Function Test (LFT) Test Overview
Blood tests for liver function tests measure the proteins, enzymes, and bilirubin your liver produces. Different chemicals can signal various diseases by having high or low quantities.
The liver is a large organ located in the upper right of the belly; the liver is essential for a variety of processes. For instance, it breaks down drugs and alcohol, filters hazardous compounds, stores vitamins and minerals, and produces bile, proteins, and enzymes in addition to other functions. Liver Function Test (LFT) Tests look at proteins, enzymes, and other elements that reveal how efficiently the liver operates. They can demonstrate whether there is liver cell injury or an obstruction of the liver's blood supply.
The liver filters all blood that exits the stomach and intestines. The liver processes this blood, breaking down, balancing, and creating nutrients, as well as metabolising medications into forms that are easier for the rest of the body to use or are harmless.
Depending on the test, these enzymes or proteins may have greater or lower levels than normal, which could indicate a liver problem. To check for diseases like hepatitis, monitor drug side effects, and determine the degree of liver disease, liver function tests may be performed for several different purposes.
What is Liver Function Test (LFT) used for?
Multiple tests are performed simultaneously on a single blood sample. Let us see the different types of liver function tests:
- Alanine transaminase (ALT) test - Your body uses an enzyme called alanine transaminase (ALT) to metabolise protein. If the liver is damaged or not functioning properly, ALT may be released into the blood. Levels of ALT rise as a result. A higher level indicates liver damage.
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) test - An enzyme called aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is present in many areas of the body, including the heart, brain, pancreas, liver, and muscles. AST can pass in circulation when the liver is damaged. An elevated AST test result could point to a liver or muscle tissue.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) test - Your bones, bile ducts, and liver all contain the enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP). An ALP test is frequently requested along with several other assays. The liver's bile duct system can be assessed with an ALP test.
- Albumin test - The primary protein produced by your liver is albumin. It is responsible for a range of critical body processes. Albumin nourishes your tissues and transports chemicals, hormones, and other substances throughout your body. An albumin test determines how well your liver generates this specific protein.
- Bilirubin test - A by-product of the decomposition of red blood cells is bilirubin. Normally, the liver is the one that processes it. Before being eliminated through faeces, it goes through the liver. Bilirubin processing is impaired in a damaged liver. As a result, the blood's bilirubin level is abnormally high. Some hereditary disorders might cause elevated bilirubin levels even when liver function is normal.
- Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) - GGT is an enzyme found in the blood. Higher-than-normal levels could indicate bile duct or liver dysfunction.
- L-lactate dehydrogenase (LD) - The liver contains the enzyme LD. However, in addition to liver damage, elevated levels can also be found in many other diseases.
- Prothrombin time (PT) - The time it takes for your blood to clot is known as PT- Prothrombin time. The use of specific blood thinners like warfarin can also cause increased PT, which can be a symptom of liver damage.
Your healthcare physician can learn vital details from these measurements about your liver's overall health and function.
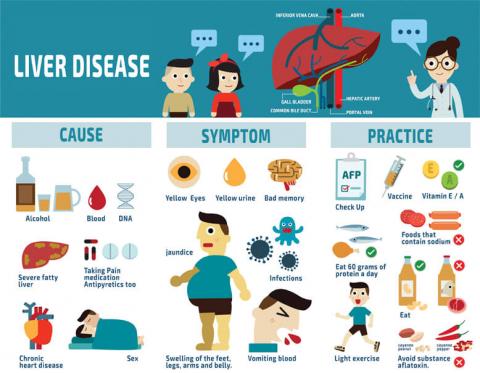
Why do you require tests for Liver Function tests (LFT)?
A liver function test (LFL) is required for the following:
- To observe jaundice, your skin and eyes turn yellow
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Stomachache or swelling
- Urine with a deep colour
- Stool with a light colour
- Fatigue
If you have particular risk factors, you could also require these tests. You might be more susceptible to liver disease if you:
- A history of family liver illness
- Loss of appetite
- Alcohol use disorder, a condition that makes it difficult to regulate one's drinking habits
- Possibility of hepatitis virus carrier
- Medications that could harm your liver
What sorts of information may a liver panel provide?
Your healthcare provider may learn the following from varying quantities and ratios of various substances:
- If your liver is inflamed (hepatitis)
- Whether the inflammation is caused by alcohol or not (metabolic)
- If your bile ducts or your liver have any issues
- If your liver function is compromised
- If your bile flow is damaged
- Certain medicines are affecting your liver
- Diabetes
- High triglycerides
- Anaemia
- High blood pressure
How are Liver Function tests (LFT) done?
Results of Liver Function tests (LFT)
For normal liver function tests, normal blood test outcomes include:
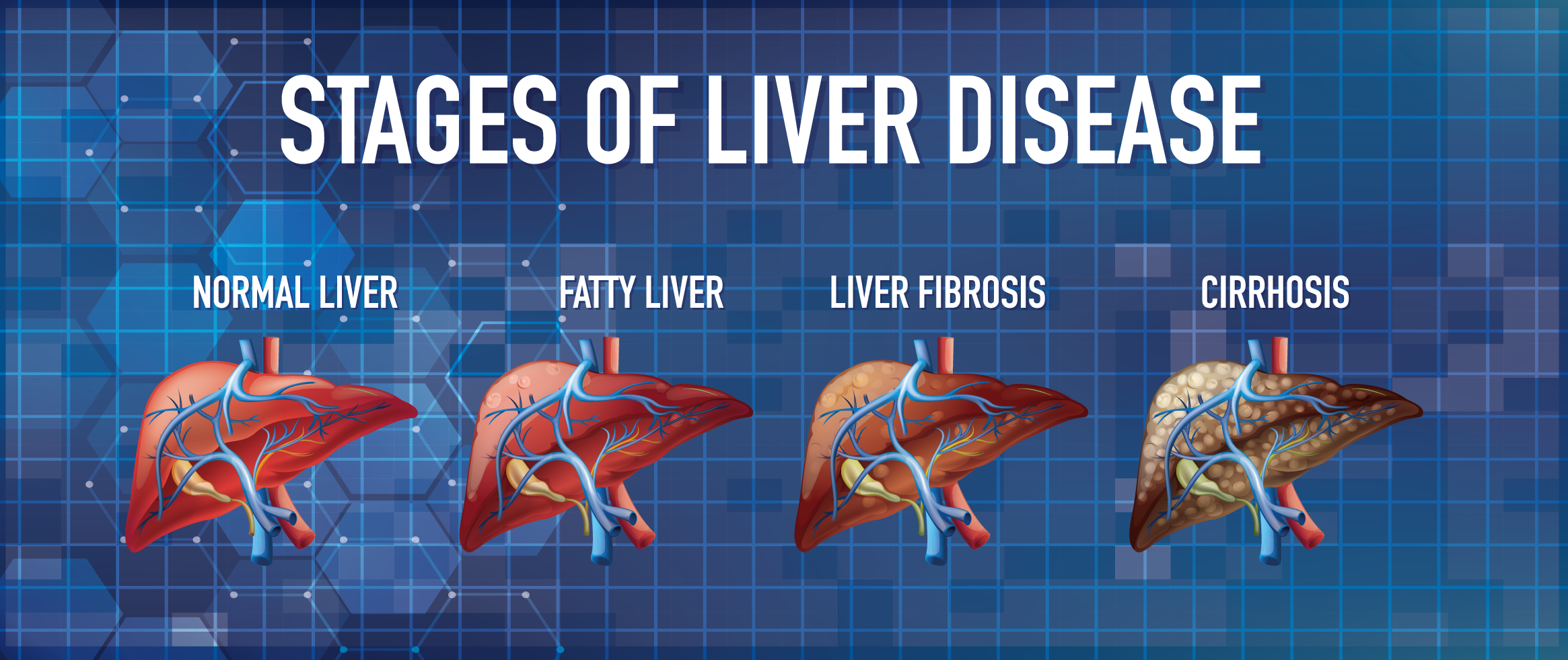
For adult males, these results are typical. Normal reports range from lab to test and may be somewhat different for females and children. These levels are used by your doctor to assist make a diagnosis or deciding if you require treatment. Numerous disorders can harm the liver, including:
Some LFTs can be influenced by circumstances in the bones or elsewhere in the body. It is also possible that certain LFT results will be marginally anomalous when there is no problem at all. You should review the results with your doctor to determine what they mean in your specific circumstances.
A medical professional will use a tiny needle to take blood from a vein in your arm.
When the needle enters or leaves your body, it could sting a little. Typically, it simply requires a few minutes.
Following your blood sample is sent to a lab for evaluation by your technician.
As long as you are not feeling lightheaded from the blood draw, you can go home after the test, resume your medications and have something to eat and drink.
ALT: 7 to 55 U/L
ALP: 40 to129 U/L
Albumin; 3.5 and 5.5 g/dL
AST: 8 to 48 IU/L
Total protein: 6.3 to 7.9 g/dL
Bilirubin: 0.1 to 1.2 mg/dL
LD: 122 to 222 U/L
GGT: 8 to 61 U/L
PT: 9.4 to 12.5 seconds
Influenza A
The hepatitis B virus
Alcoholism is a component of the hepatitis C alcohol use disorder.
Liver tumour
Diabetes




 NABL approved
NABL approved  Most Trusted by
Most Trusted by  Accuracy &
Accuracy &  Widest Range
Widest Range 





















































.webp)











