Triglycerides

Gender for Male, Female

Report Tat
2Hrs Same Day
No special preparation required

Sample Type
Serum
Test Overview
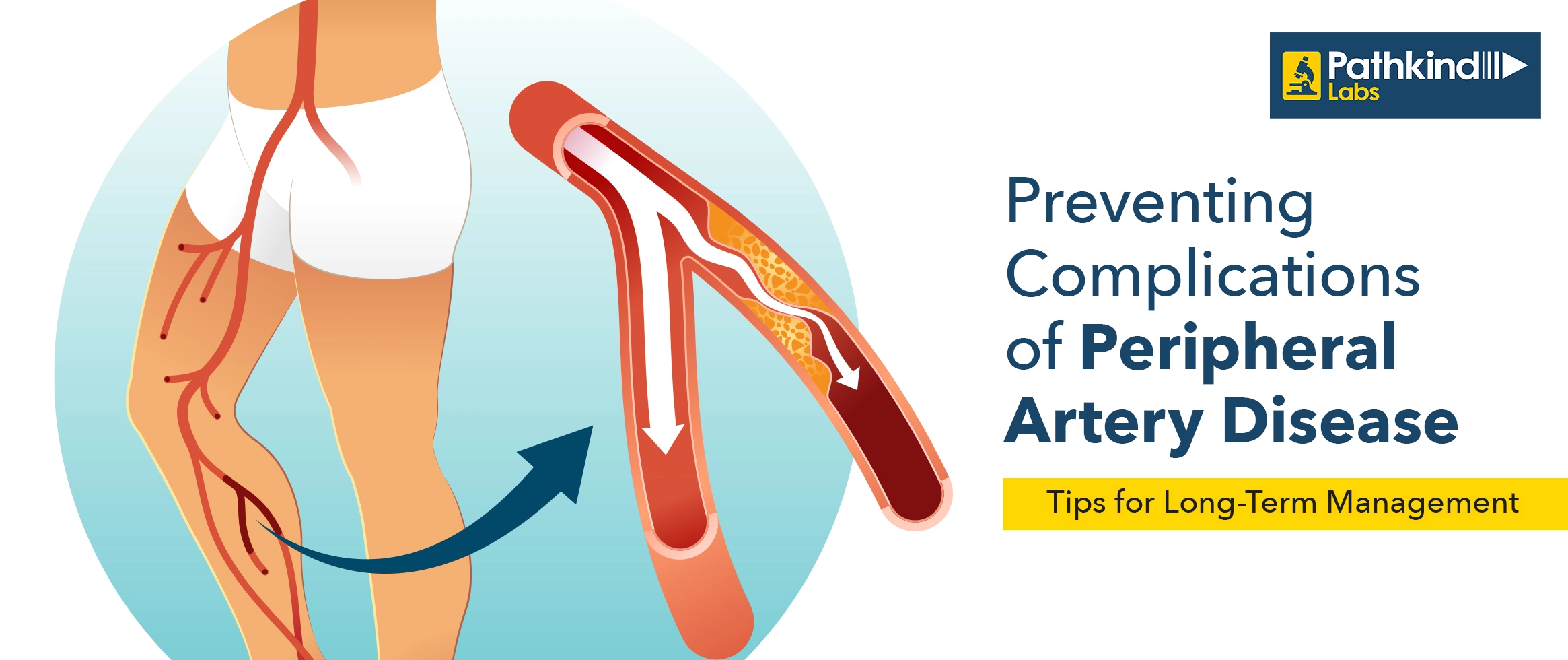
The Triglycerides test measures the amount of triglycerides in your blood, an essential indicator of your heart health. High triglyceride levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases and other metabolic conditions.

 NABL approved
NABL approved Labs
 Most Trusted by
Most Trusted by Doctors
 Accuracy &
Accuracy & timely reporting
 Widest Range
Widest Range of Tests
Test Details
Frequently asked questions
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in your blood, derived from the food you eat.
The normal level of triglycerides is less than 150 mg/dL.
Yes, fasting for 9-12 hours is generally required for accurate results.
Elevated triglycerides can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.